Threonine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
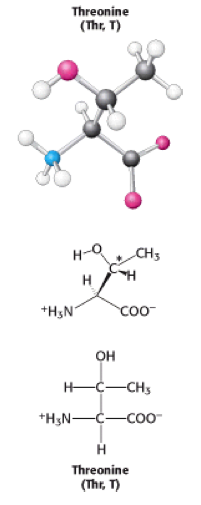
Threonine is an uncharged, polar [[Amino acids|amino acid]] whose three letter code is Thr and single letter code is T. It interacts with other polar molecules using [[ | [[Image:Threonine.png]] | ||
Threonine is an uncharged, polar [[Amino acids|amino acid]] whose three letter code is Thr and single letter code is T. It interacts with other polar molecules using [[Hydrogen bonds|hydrogen bonds]]. Its [[Hydroxyl group|hydroxyl]] group is polar and its R group is uncharged and is C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>5</sub>O <ref>Lodish, H et al., 2008, Molecular Cell Biology, Sixth edition, 42-43, New York,NY:WH Freeman and Company.</ref>. | |||
=== References === | === References === | ||
< | Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.<br> | ||
Revision as of 14:39, 29 November 2013
Threonine is an uncharged, polar amino acid whose three letter code is Thr and single letter code is T. It interacts with other polar molecules using hydrogen bonds. Its hydroxyl group is polar and its R group is uncharged and is C2H5O [1].
References
Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.
- ↑ Lodish, H et al., 2008, Molecular Cell Biology, Sixth edition, 42-43, New York,NY:WH Freeman and Company.