Endothelial cell: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Added extra Information about the topic, added references and inserted a diagram. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Endothelial cells make up the [[ | Endothelial cells make up the [[Endothelium|endothelium]] which lines the inner surface of the [[Lymphatic system|lymphatic system]], [[Blood vessels|blood vessels]] and also the [[Heart|heart]]. Among their functions are coagulation, blood vessel formation, inflammation, relaxation of arterial smooth muscle and [[Fibrinolysis|fibrinolysis]] <ref>Michiels, C. (2003) Endothelial Cell Functions.Journal of Cellular Physiology. 196(3). pp. 430-432</ref>.<br> | ||
There is a varying number between the amount of [[Smooth Muscle|smooth muscle]] and [[Connective tissue|connective tissue]] because different vessels that carry out distinct functions and have different structure. As an example, bigger diameter more smooth muscle and more connective tissues are available e.g. [[Artery|Artery]]<ref>Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Wilson, J. and Hunt, T. (2015). Molecular biology of the cell. 6th ed. Abingdon: Garland Science, Taylor &amp;amp; Francis Group, p. 1235.</ref>. | |||
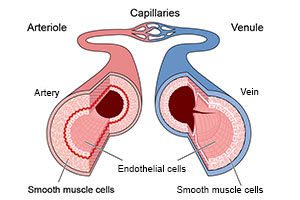
<references /> | [[Image:Endothelial-cells-functions.jpg|Figure 1 - Corss-section diagram of blood vessels]] | ||
Figure 1 - Corss-section diagram of blood vessels<ref>Lonza.com. (2017). Endothelial Cells and Functions. [online] Available at: https://www.lonza.com/campaigns/bioresearch/endothelium-cells-and-functions.aspx [Accessed 4 Dec. 2017].</ref>. | |||
<br> | |||
References: | |||
<references /><br> | |||
<references /> | |||
<references /> | |||
<br> | |||
Revision as of 20:54, 4 December 2017
Endothelial cells make up the endothelium which lines the inner surface of the lymphatic system, blood vessels and also the heart. Among their functions are coagulation, blood vessel formation, inflammation, relaxation of arterial smooth muscle and fibrinolysis [1].
There is a varying number between the amount of smooth muscle and connective tissue because different vessels that carry out distinct functions and have different structure. As an example, bigger diameter more smooth muscle and more connective tissues are available e.g. Artery[2].
Figure 1 - Corss-section diagram of blood vessels[3].
References:
- ↑ Michiels, C. (2003) Endothelial Cell Functions.Journal of Cellular Physiology. 196(3). pp. 430-432
- ↑ Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Wilson, J. and Hunt, T. (2015). Molecular biology of the cell. 6th ed. Abingdon: Garland Science, Taylor &amp; Francis Group, p. 1235.
- ↑ Lonza.com. (2017). Endothelial Cells and Functions. [online] Available at: https://www.lonza.com/campaigns/bioresearch/endothelium-cells-and-functions.aspx [Accessed 4 Dec. 2017].