Haploid cell: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Reformatted the page. Cleaned up the text. Added a lot of links. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Snip20171203 2.png|right|Snip20171203 2.png]] Haploid cells contain a single set of [[chromosomes|chromosomes]]. | |||
Gametes are an example of haploid [[cells|cells]] produced as a result of [[meiosis|meiosis]]. | |||
Examples of [[gametes|gametes]] are the [[male|male]] and [[female|female]] reproductive cells, the [[sperm|sperm]] and [[egg|egg]] cell respectively. | |||
The number of chromosomes in these gametes are 23 (n), while [[diploid cell|diploid cells]] contain 46 (2n) chromosomes. | |||
[[ | [[Organisms|Organisms]] that have a haploid life cycle include most [[fungi|fungi]] (with [[dikaryotic phase|dikaryotic phase]]), [[algae|algae]] (without dikaryotic phase) and male ants and bees<ref>Scitable by nature education. Definition Haploid. 2014 [cited 3/12/17]; Available from: https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/haploid-309</ref>. | ||
=== References === | |||
=== References | |||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:19, 4 December 2017
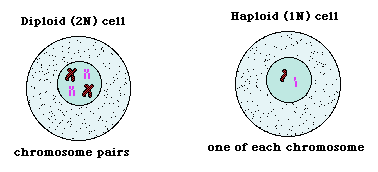
Haploid cells contain a single set of chromosomes.
Gametes are an example of haploid cells produced as a result of meiosis.
Examples of gametes are the male and female reproductive cells, the sperm and egg cell respectively.
The number of chromosomes in these gametes are 23 (n), while diploid cells contain 46 (2n) chromosomes.
Organisms that have a haploid life cycle include most fungi (with dikaryotic phase), algae (without dikaryotic phase) and male ants and bees[1].
References
- ↑ Scitable by nature education. Definition Haploid. 2014 [cited 3/12/17]; Available from: https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/haploid-309