Proline: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
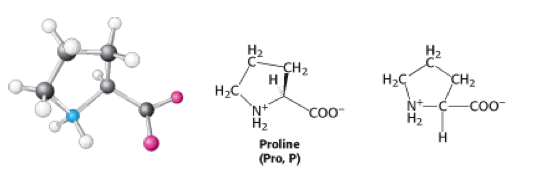
Proline is an amino acid. It has a molecular weight of 115.13 g/mol and its molecular formula is C<sub>5</sub>H<sub>9</sub>NO<sub>2</sub>. It is also classified as a [[Hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] amino acid. It is also known as imino acid. | |||
Proline has an [[Aliphatic|aliphatic]] side chain, which is bonded to the nitrogen atom and the [[Alpha-carbon|alpha-carbon]] [[Atom|atom]]. It influences [[Protein|protein]] architecture, because it's structure makes it more conformationally restricted than other [[Amino acids|amino acids]]<ref>Biochemistry 6th ed. 2006, J.Berg ''et al.''</ref>. | |||
Four codons translate for Proline, they are: CCU, CCC, CCA and CCG. | |||
[[Image:Proline.png]] | |||
=== References === | === References === | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:35, 3 December 2018
Proline is an amino acid. It has a molecular weight of 115.13 g/mol and its molecular formula is C5H9NO2. It is also classified as a hydrophobic amino acid. It is also known as imino acid.
Proline has an aliphatic side chain, which is bonded to the nitrogen atom and the alpha-carbon atom. It influences protein architecture, because it's structure makes it more conformationally restricted than other amino acids[1].
Four codons translate for Proline, they are: CCU, CCC, CCA and CCG.
References
- ↑ Biochemistry 6th ed. 2006, J.Berg et al.