Isoleucine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with 'Isoleucine is a hydrophobic neutral amino acid, the reason why its hydrophilic is because it has a aliphatic side chain. Isoleucine has an additional chiral centre at c…' |
Cleaned up the references. |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Isoleucine | [[Image:Isoleucine.png|right|Isoleucine.png]] | ||
< | Isoleucine is a [[Hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] neutral [[Amino acids|amino acid]], the reason why it is [[Hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] is because it has an [[Aliphatic|aliphatic]] side chain. Due to this hydrophobic characteristic of the amino acid, it interacts more favourably with other [[Aliphatic|aliphatic]] [[Amino acid residues|residues]], such as: alanine, valine and leucine, and other [[Non-polar amino acids|non-polar amino acids]]. This is one of the main factors in stabilizing the folded conformations of proteins<ref>Proteins structures and molecular properties, second edition, Thomas E. Creighton... pg 7</ref>. Isoleucine has an additional [[Chiral centre|chiral centre]] at [[Carbon|carbon]] 3<ref>Berg J., Tymoczko J and Stryer L. (2007) Biochemistry, 6th edition, New York: WH Freeman</ref><ref>Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., and Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.</ref>. | ||
References | === References === | ||
<references /> | |||
Latest revision as of 09:01, 10 December 2018
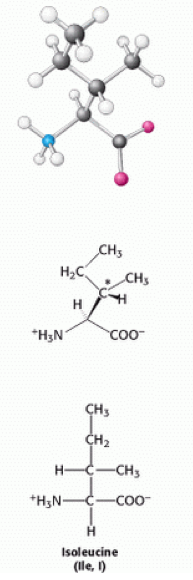
Isoleucine is a hydrophobic neutral amino acid, the reason why it is hydrophobic is because it has an aliphatic side chain. Due to this hydrophobic characteristic of the amino acid, it interacts more favourably with other aliphatic residues, such as: alanine, valine and leucine, and other non-polar amino acids. This is one of the main factors in stabilizing the folded conformations of proteins[1]. Isoleucine has an additional chiral centre at carbon 3[2][3].