Chiasma: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
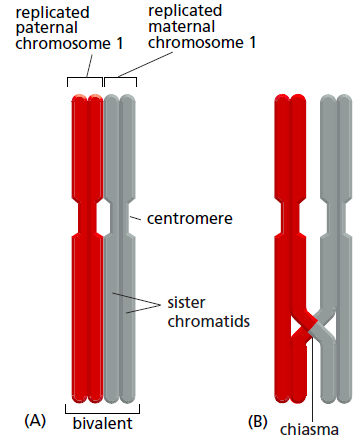
Chiasma or crossover refers to the visible point where paired maternal and paternal [[Homologous chromosome|homologous]] [[Homologous chromosomes|chromosomes]] join during [[Meiosis|meiosis ]]1 and then crossover. This [[Recombination|recombination]] occurs when a segment of one paternal [[Chromatid|chromatid]] is replaced by the [[Complementary|complementary]] form of the other maternal [[Chromatid|chromatid]] <ref>Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts and Peter Walter, 2008. Molecular biology of the cell. 5th edition. New York: Garland science.</ref>. | |||
There are 2 [[Nuclear division|nuclear divisions]] in [[Meiosis|meiosis]], and a chiasma forms in the first division of [[Meiosis|meiosis]] 1. The duplicated [[Homologues|homologs]] align with each other and swap genetic information [[Recombination|(recombination)]]. | There are 2 [[Nuclear division|nuclear divisions]] in [[Meiosis|meiosis]], and a chiasma forms in the first division of [[Meiosis|meiosis]] 1. The duplicated [[Homologues|homologs]] align with each other and swap genetic information [[Recombination|(recombination)]]. | ||
Crossover happens between 2 non-sister [[Chromatids|chromatids]]. The chiasma can be seen at the point where the [[Homologues|homologs]] join in [[Prophase|prophase]] 1, when the [[Synaptonemal Complex|synaptonemal complex]] disassembles and | Crossover happens between 2 non-sister [[Chromatids|chromatids]]. The chiasma can be seen during the diplotene stage, at the point where the [[Homologues|homologs]] join in [[Prophase|prophase]] 1, when the [[Synaptonemal Complex|synaptonemal complex]] disassembles and begin to separate''.'' They crucially hold the compact homologues together<ref>Alberts, B. 2008. Molecular biology of the cell. New York: Garland Science.</ref>. The frequency of crossing over varies, with the occurrence in humans being at least once in each chromosome arm. | ||
[[Image:Screen Shot 2013-11-27 at 15.23.19.png|Homologous pair of chromosomes showing chiasma]] | |||
=== References === | |||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:08, 1 December 2013
Chiasma or crossover refers to the visible point where paired maternal and paternal homologous chromosomes join during meiosis 1 and then crossover. This recombination occurs when a segment of one paternal chromatid is replaced by the complementary form of the other maternal chromatid [1].
There are 2 nuclear divisions in meiosis, and a chiasma forms in the first division of meiosis 1. The duplicated homologs align with each other and swap genetic information (recombination).
Crossover happens between 2 non-sister chromatids. The chiasma can be seen during the diplotene stage, at the point where the homologs join in prophase 1, when the synaptonemal complex disassembles and begin to separate. They crucially hold the compact homologues together[2]. The frequency of crossing over varies, with the occurrence in humans being at least once in each chromosome arm.