Smooth muscle cells: Difference between revisions
Created page with "[http://www.cytochemistry.net/microanatomy/muscle/smooth_muscle_2001.htm http://www.cytochemistry.net/microanatomy/muscle/smooth_muscle_2001.htm][[Image:Smooth muscle contraction..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[http://www.cytochemistry.net/microanatomy/muscle/smooth_muscle_2001.htm http://www.cytochemistry.net/microanatomy/muscle/smooth_muscle_2001.htm][[Image:Smooth muscle contraction.jpg|Diagram showing the contraction of a smooth muscle cell]] | [http://www.cytochemistry.net/microanatomy/muscle/smooth_muscle_2001.htm http://www.cytochemistry.net/microanatomy/muscle/smooth_muscle_2001.htm][[Image:Smooth muscle contraction.jpg|Diagram showing the contraction of a smooth muscle cell]] | ||
Smooth muscle cells are long and thin in structure and arrange around tissues in layers. They do not conain any sarcomeres and few nuclei but myosin is scattered throughout the cell. Dense-bodies attach to actin filaments in the muscle sarcoplasm, this prevents the actin molecules moving during contraction. The dense-bodies also connect other smooth muscle cellsand are arranged randomly throughout the fibres. | |||
Smooth muscle cells are found in blood vessels, gut, skin, eye pupils, urinary and reproductive tracts. This means they are able to regulate blood flow and movement of substances through different blood vessels. The contraction of smooth muscle cells is involuntary and slower however it is more controlled than the contraction of skeletal muscle cells. | |||
Revision as of 13:38, 1 December 2011
http://www.cytochemistry.net/microanatomy/muscle/smooth_muscle_2001.htm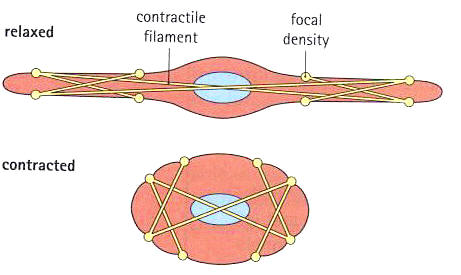
Smooth muscle cells are long and thin in structure and arrange around tissues in layers. They do not conain any sarcomeres and few nuclei but myosin is scattered throughout the cell. Dense-bodies attach to actin filaments in the muscle sarcoplasm, this prevents the actin molecules moving during contraction. The dense-bodies also connect other smooth muscle cellsand are arranged randomly throughout the fibres.
Smooth muscle cells are found in blood vessels, gut, skin, eye pupils, urinary and reproductive tracts. This means they are able to regulate blood flow and movement of substances through different blood vessels. The contraction of smooth muscle cells is involuntary and slower however it is more controlled than the contraction of skeletal muscle cells.