Isoleucine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
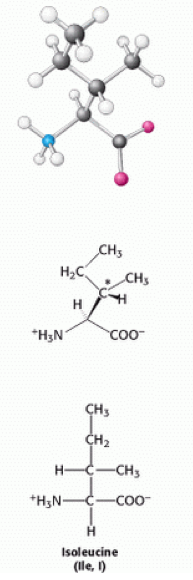
Isoleucine is a [[Hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] neutral [[Amino acids|amino acid]], the reason why it is [[hydrophilic|hydrophilic]] is because it has an [[Aliphatic|aliphatic]] side chain. Isoleucine has an additional [[Chiral centre|chiral centre]] at [[Carbon|carbon]] 3 <ref>Berg J., Tymoczko J and Stryer L. (2007) Biochemistry, 6th edition, New York: WH Freeman</ref>.<br> | Isoleucine is a [[Hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] neutral [[Amino acids|amino acid]], the reason why it is [[hydrophilic|hydrophilic]] is because it has an [[Aliphatic|aliphatic]] side chain. Isoleucine has an additional [[Chiral centre|chiral centre]] at [[Carbon|carbon]] 3 <ref>Berg J., Tymoczko J and Stryer L. (2007) Biochemistry, 6th edition, New York: WH Freeman</ref>.<br> | ||
[[Image:Isoleucine.png]] | |||
=== References === | === References === | ||
Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.<br> | |||
Revision as of 14:34, 29 November 2013
Isoleucine is a hydrophobic neutral amino acid, the reason why it is hydrophilic is because it has an aliphatic side chain. Isoleucine has an additional chiral centre at carbon 3 [1].
References
Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.
- ↑ Berg J., Tymoczko J and Stryer L. (2007) Biochemistry, 6th edition, New York: WH Freeman