Proline: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
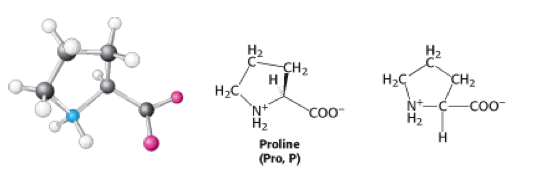
<sub></sub>Proline has an [[Aliphatic|aliphatic]] side chain, which is bonded to the nitrogen atom and the [[Alpha-carbon|alpha-carbon]] [[atom|atom]]. It influences [[Protein|protein]] architecture, because it's structure makes it more conformationally restricted than other [[Amino acids|amino acids]] <ref>Biochemistry 6th ed. 2006, J.Berg et al</ref>. It is also a [[hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] amino acid.<br> | <sub></sub>Proline has an [[Aliphatic|aliphatic]] side chain, which is bonded to the nitrogen atom and the [[Alpha-carbon|alpha-carbon]] [[atom|atom]]. It influences [[Protein|protein]] architecture, because it's structure makes it more conformationally restricted than other [[Amino acids|amino acids]] <ref>Biochemistry 6th ed. 2006, J.Berg et al</ref>. It is also a [[hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] amino acid.<br> | ||
[[Image:Proline.png]] | |||
=== References === | === References === | ||
< | Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.<br> | ||
Revision as of 14:36, 29 November 2013
Not an amino acid...........(It is actually an imino acid!)
Due it being joined to itself back on to the nitrogen. Its molecular formula is C5H9NO2.
Proline has an aliphatic side chain, which is bonded to the nitrogen atom and the alpha-carbon atom. It influences protein architecture, because it's structure makes it more conformationally restricted than other amino acids [1]. It is also a hydrophobic amino acid.
References
Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.
- ↑ Biochemistry 6th ed. 2006, J.Berg et al