Phenylalanine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Phenylalanine.png]] | [[Image:Phenylalanine.png|169x584px]] | ||
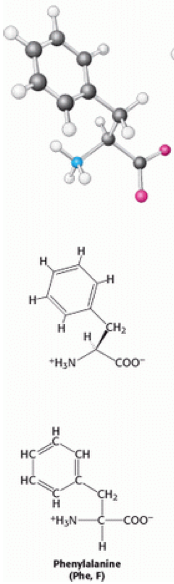
Phenylalanine contains a benzyl side chain, giving it a [[Hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] nature that gives it the classification of [[Non-polar|non-polar]]. | Phenylalanine (also known as Phe or F) is a non-polar aromatic α-amino acid, with the formula C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>CH(NH<sub>2</sub>)COOH. There are three types of phenylalanine, D-phenylalanine, L-phenylalanine and DL-phenylalanine. Phenylalanine contains a benzyl side chain, giving it a [[Hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] nature that gives it the classification of [[Non-polar|non-polar]]. References | ||
<references /><br> | <references /><br> | ||
Revision as of 16:33, 25 November 2014
Phenylalanine (also known as Phe or F) is a non-polar aromatic α-amino acid, with the formula C6H5CH2CH(NH2)COOH. There are three types of phenylalanine, D-phenylalanine, L-phenylalanine and DL-phenylalanine. Phenylalanine contains a benzyl side chain, giving it a hydrophobic nature that gives it the classification of non-polar. References