COPD: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Copd lung1.jpg|border|right|127x89px|Postmortem dissection of lungs affected by COPD]]COPD – Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary (from Latin: pulmo/pulmonis "Lung/Lungs") Disease is an incurable life-threatening airway disease, causing over 3 million deaths, which is 5% of all deaths in the world in the year 2005 <ref>WHO (2009) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs315/en/index.html (Accessed: 23.11.2010).</ref>. The term COPD is commonly referred to a number of [[Lung|lung]] diseases, such as [[Chronic bronchitis|chronic bronchitis]] and [[Emphysema|emphysema]], when airways in the lungs become clogged with [[Mucus|mucus]], narrowed by inflammation, damaged or lose their elasticity, resulting in less air reaching the lungs leading to shortness of breath in patients.<ref>U.S. National Heart Lung and Blood Institute - What is COPD 2010. Available at: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/Copd/Copd_WhatIs.html (Accessed: 23.11.2010).</ref><br> | [[Image:Copd lung1.jpg|border|right|127x89px|Postmortem dissection of lungs affected by COPD]]'''COPD''' – '''Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary''' (''from Latin'': ''pulmo/pulmonis'' "''Lung/Lungs''") '''Disease''' is an incurable life-threatening airway disease, causing over 3 million deaths, which is 5% of all deaths in the world in the year 2005 <ref>WHO (2009) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs315/en/index.html (Accessed: 23.11.2010).</ref>. The term COPD is commonly referred to a number of [[Lung|lung]] diseases, such as [[Chronic bronchitis|chronic bronchitis]] and [[Emphysema|emphysema]], when airways in the lungs become clogged with [[Mucus|mucus]], narrowed by inflammation, damaged or lose their elasticity, resulting in less air reaching the lungs leading to shortness of breath in patients.<ref>U.S. National Heart Lung and Blood Institute - What is COPD 2010. Available at: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/Copd/Copd_WhatIs.html (Accessed: 23.11.2010).</ref><br> | ||
=== References === | === References === | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 12:17, 23 November 2010
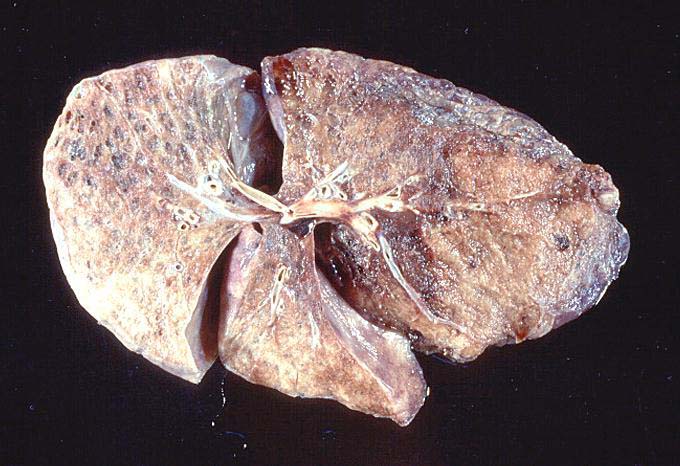
COPD – Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary (from Latin: pulmo/pulmonis "Lung/Lungs") Disease is an incurable life-threatening airway disease, causing over 3 million deaths, which is 5% of all deaths in the world in the year 2005 [1]. The term COPD is commonly referred to a number of lung diseases, such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema, when airways in the lungs become clogged with mucus, narrowed by inflammation, damaged or lose their elasticity, resulting in less air reaching the lungs leading to shortness of breath in patients.[2]
References
- ↑ WHO (2009) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs315/en/index.html (Accessed: 23.11.2010).
- ↑ U.S. National Heart Lung and Blood Institute - What is COPD 2010. Available at: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/Copd/Copd_WhatIs.html (Accessed: 23.11.2010).