Heart: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Heart.jpg|frame|right]] | [[Image:Heart.jpg|frame|right|Heart.jpg]] | ||
The heart is the driving force of the [[The Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular System]] and is found in the human body in the left of the centre (between the [[Lungs|lungs]]). The heart function is to pump oxygenated [[Blood|blood]] around the body through arteries and to accept deoxygenated [[Blood|blood]] through the veins. These two processes are separated into the heart's left and right hand side respectively<ref>Parker S. (2007) The Human Body Book, 1st edition, London: Dorling Kindersley Limited.</ref> which are subdivided into four chambers <ref name="image">http://www.gknmhospital.org/ctvs/hevaldis.html</ref>. Temporal dispersion of recovery of excitability, measured as the range of local refractory period durations at numerous sites on the atrial and ventricular surfaces, was found to be a direct function of the basic cycle length except at very rapid driving frequencies<ref>Han et al. Temporal Dispersion Of Recovery Of Excitability In Atrium And Ventricle As A Function Of Heart Rate'. American Heart Journal 71.4 (1966): 481-487. Web.The Upper chambers are known as the [[Atria|Atria]], and the lower chambers are called [[Ventricles|ventricles]]&amp;amp;amp;nbsp;&amp;amp;lt;ref&amp;amp;gt;http://inspirations786.wordpress.com/2011/11/15/four-chambers-of-heart-islamic-polygamy-of-up-to-four-wives-and-miracle-of-allah/</ref>. The wall separating the [[Ventricles|ventricles]] is known as the [[Ventricular septum|ventricular septum]] <ref>http://www.gknmhospital.org/ctvs/hevaldis.html</ref>. The heart is essentially a muscle. The ventricles have thick muscular wall in comparison the atria. This is because the ventricles are required to send the blood all round the body rather than just to the lungs. This requires a greater force, so hence more muscle is required to provide this. <ref>http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hhw/anatomy</ref> | The heart is the driving force of the [[The Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular System]] and is found in the human body in the left of the centre (between the [[Lungs|lungs]]). The heart function is to pump oxygenated [[Blood|blood]] around the body through arteries and to accept deoxygenated [[Blood|blood]] through the veins. These two processes are separated into the heart's left and right hand side respectively<ref>Parker S. (2007) The Human Body Book, 1st edition, London: Dorling Kindersley Limited.</ref> which are subdivided into four chambers <ref name="image">http://www.gknmhospital.org/ctvs/hevaldis.html</ref>. Temporal dispersion of recovery of excitability, measured as the range of local refractory period durations at numerous sites on the atrial and ventricular surfaces, was found to be a direct function of the basic cycle length except at very rapid driving frequencies<ref>Han et al. Temporal Dispersion Of Recovery Of Excitability In Atrium And Ventricle As A Function Of Heart Rate'. American Heart Journal 71.4 (1966): 481-487. Web.The Upper chambers are known as the [[Atria|Atria]], and the lower chambers are called [[Ventricles|ventricles]]&amp;amp;amp;amp;nbsp;&amp;amp;amp;lt;ref&amp;amp;amp;gt;http://inspirations786.wordpress.com/2011/11/15/four-chambers-of-heart-islamic-polygamy-of-up-to-four-wives-and-miracle-of-allah/</ref>. The wall separating the [[Ventricles|ventricles]] is known as the [[Ventricular septum|ventricular septum]] <ref>http://www.gknmhospital.org/ctvs/hevaldis.html</ref>. The heart is essentially a muscle. The ventricles have thick muscular wall in comparison the atria. This is because the ventricles are required to send the blood all round the body rather than just to the lungs. This requires a greater force, so hence more muscle is required to provide this. <ref>http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hhw/anatomy</ref> | ||
The ventricles are the bottom 2 chambers of the heart with the atrium being the top two chambers of the heart. The left atrium is located on the left posterior side. Its main roles are to act as a holding chamber for blood returning from the lungs sas well as to act as a pump to transport blood to other areas of the heart.The right atrium is located on the top right hand side nex to the superior vena cava. Its primary function if for allowing deoxygenated blood to enter through the inferior and superior vena cava. The right side of the heart then pumps this deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary veins around the lungs.<ref name="http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/right-atrium">Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the inferior and superior vena cava. The right side of the heart then pumps this deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary veins around the lungs.</ref> | The ventricles are the bottom 2 chambers of the heart with the atrium being the top two chambers of the heart. The left atrium is located on the left posterior side. Its main roles are to act as a holding chamber for blood returning from the lungs sas well as to act as a pump to transport blood to other areas of the heart.<ref name="http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/left-atrium">ocated on the left posterior side. Its primary roles are to act as a holding chamber for blood returning from the lungs and to act as a pump to transport blood to other areas of the heart</ref> The right atrium is located on the top right hand side nex to the superior vena cava. Its primary function if for allowing deoxygenated blood to enter through the inferior and superior vena cava. The right side of the heart then pumps this deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary veins around the lungs.<ref name="http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/right-atrium">Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the inferior and superior vena cava. The right side of the heart then pumps this deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary veins around the lungs.</ref> | ||
For the heart to function properly it should be healthy. A healthy heart will circulate blood through out the body at the right pace providing sufficiently to all parts of the body. This vital organ is unable to perform this necessary function if weakened by disease or injury<ref>http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hhw</ref>.<sup></sup><br> | For the heart to function properly it should be healthy. A healthy heart will circulate blood through out the body at the right pace providing sufficiently to all parts of the body. This vital organ is unable to perform this necessary function if weakened by disease or injury<ref>http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hhw</ref>.<sup></sup><br> | ||
=== References:<br> === | === References:<br> === | ||
Revision as of 12:17, 4 December 2015
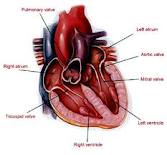
The heart is the driving force of the Cardiovascular System and is found in the human body in the left of the centre (between the lungs). The heart function is to pump oxygenated blood around the body through arteries and to accept deoxygenated blood through the veins. These two processes are separated into the heart's left and right hand side respectively[1] which are subdivided into four chambers [2]. Temporal dispersion of recovery of excitability, measured as the range of local refractory period durations at numerous sites on the atrial and ventricular surfaces, was found to be a direct function of the basic cycle length except at very rapid driving frequencies[3]. The wall separating the ventricles is known as the ventricular septum [4]. The heart is essentially a muscle. The ventricles have thick muscular wall in comparison the atria. This is because the ventricles are required to send the blood all round the body rather than just to the lungs. This requires a greater force, so hence more muscle is required to provide this. [5]
The ventricles are the bottom 2 chambers of the heart with the atrium being the top two chambers of the heart. The left atrium is located on the left posterior side. Its main roles are to act as a holding chamber for blood returning from the lungs sas well as to act as a pump to transport blood to other areas of the heart.[6] The right atrium is located on the top right hand side nex to the superior vena cava. Its primary function if for allowing deoxygenated blood to enter through the inferior and superior vena cava. The right side of the heart then pumps this deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary veins around the lungs.[7]
For the heart to function properly it should be healthy. A healthy heart will circulate blood through out the body at the right pace providing sufficiently to all parts of the body. This vital organ is unable to perform this necessary function if weakened by disease or injury[8].
References:
- ↑ Parker S. (2007) The Human Body Book, 1st edition, London: Dorling Kindersley Limited.
- ↑ http://www.gknmhospital.org/ctvs/hevaldis.html
- ↑ Han et al. Temporal Dispersion Of Recovery Of Excitability In Atrium And Ventricle As A Function Of Heart Rate'. American Heart Journal 71.4 (1966): 481-487. Web.The Upper chambers are known as the Atria, and the lower chambers are called ventricles&amp;amp;amp;nbsp;&amp;amp;lt;ref&amp;amp;gt;http://inspirations786.wordpress.com/2011/11/15/four-chambers-of-heart-islamic-polygamy-of-up-to-four-wives-and-miracle-of-allah/
- ↑ http://www.gknmhospital.org/ctvs/hevaldis.html
- ↑ http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hhw/anatomy
- ↑ ocated on the left posterior side. Its primary roles are to act as a holding chamber for blood returning from the lungs and to act as a pump to transport blood to other areas of the heart
- ↑ Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the inferior and superior vena cava. The right side of the heart then pumps this deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary veins around the lungs.
- ↑ http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hhw