Parkinson's Disease: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
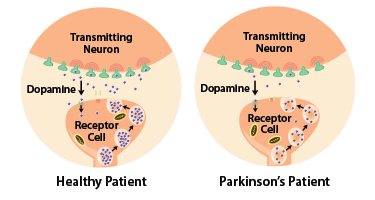
Parkinson’s disease, also known as hypokinetic rigid syndrome (HRS), is an [[Idiopathic|idiopathic]] and has no known cause. It is normally due to the degeneration of [[Dopaminergic neurone|dopaminergic neurones]] of the nigrostriatal tract and loss of [[Dopamine|dopamine]] (DA) neurotransmission in the striatum. The symptoms of this disease are a resting tremor, muscle | Parkinson’s disease, also known as hypokinetic rigid syndrome (HRS), is an [[Idiopathic|idiopathic]] and has no known cause. It is normally due to the degeneration of [[Dopaminergic neurone|dopaminergic neurones]] of the nigrostriatal tract and loss of [[Dopamine|dopamine]] (DA) neurotransmission in the striatum. The symptoms of this disease are a resting tremor, muscle rigi<span style="font-size: 13.28px;">dity, suppression of voluntary movements (hypokinesis) and postural instability. Another com</span><span style="font-size: 13.28px;">mon symptom of parkinsons</span><span style="font-size: 13.28px;"> disease is freezing which is the inability to move temporarily and can last a few seconds to several minutes. Often people feel like their feet are stuck to the ground and this occurs often when a sufferer is carrying out repetitive movements like walking, </span><span style="font-size: 13.28px;">eating or writing.</span> | ||
<span style="font-size: 13.28px;" /><span style="font-size: 13.28px;"> </span>[[Image:Parkinsons_patients_have_less_dopamine.png|Dopamine in Parkinson's Disease]]<sup></sup> | |||
<span style="font-size: 13.28px;">In the later stages, mental and behavioural problems may occur such as depression and even dementia.</span> | |||
The main 4 dopaminergic pathways are:- | The main 4 dopaminergic pathways are:- | ||
| Line 8: | Line 12: | ||
#[[Frontal cortex|Frontal cortex]] <span style="line-height: 1.5em">Tuberoinfundibular - </span>Arcuate nucleus to [[Pituitary gland|pituitary gland]] | #[[Frontal cortex|Frontal cortex]] <span style="line-height: 1.5em">Tuberoinfundibular - </span>Arcuate nucleus to [[Pituitary gland|pituitary gland]] | ||
<span style="line-height: 1.5em">The [[Decarboxylase inhibitor|decarboxylase inhibitor]] – carbidopa, the </span>[[MAO|MAO inhibitor]]<span style="line-height: 1.5em">: Selegiline and </span>[[D2 receptor|D2 receptor agonists]]<span style="line-height: 1.5em"> like [[Bromocriptine|Bromocriptine]] can be used to treat Parkinson’s disease.</span> | <span style="line-height: 1.5em">The [[Decarboxylase inhibitor|decarboxylase inhibitor]] – carbidopa, the </span>[[MAO|MAO inhibitor]]<span style="line-height: 1.5em">: Selegiline and </span>[[D2 receptor|D2 receptor agonists]]<span style="line-height: 1.5em"> like [[Bromocriptine|Bromocriptine]] can be used to treat Parkinson’s disease.</span> | ||
<span style="line-height: 1.5em" />L-DOPA is a drug often given to patients in early stages of parkinsons disease to suppress symptoms. L-DOPA is converted to dopamine in the brain therefore increasing the amount available to bind to dopamine receptors. | |||
=== References === | |||
Picture reference: <span style="font-size: 13.28px;">Parkinsons Disease. </span><span style="font-size: 13.28px;">National Institue of Environmental Health Sciences.</span> | |||
<span style="font-size: 13.28px;">Available from: </span><span style="font-size: 13.28px;">http://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/conditions/parkinson/ </span> | |||
Revision as of 13:07, 14 November 2016
Parkinson’s disease, also known as hypokinetic rigid syndrome (HRS), is an idiopathic and has no known cause. It is normally due to the degeneration of dopaminergic neurones of the nigrostriatal tract and loss of dopamine (DA) neurotransmission in the striatum. The symptoms of this disease are a resting tremor, muscle rigidity, suppression of voluntary movements (hypokinesis) and postural instability. Another common symptom of parkinsons disease is freezing which is the inability to move temporarily and can last a few seconds to several minutes. Often people feel like their feet are stuck to the ground and this occurs often when a sufferer is carrying out repetitive movements like walking, eating or writing.
In the later stages, mental and behavioural problems may occur such as depression and even dementia.
The main 4 dopaminergic pathways are:-
- Nigrostriatal - Substantia nigra to striatum
- Striatum Mesolimbic - Ventral tegmental area to nucleus accumbens
- Mesocortical - Ventral tegmental area to frontal cortex
- Frontal cortex Tuberoinfundibular - Arcuate nucleus to pituitary gland
The decarboxylase inhibitor – carbidopa, the MAO inhibitor: Selegiline and D2 receptor agonists like Bromocriptine can be used to treat Parkinson’s disease.
L-DOPA is a drug often given to patients in early stages of parkinsons disease to suppress symptoms. L-DOPA is converted to dopamine in the brain therefore increasing the amount available to bind to dopamine receptors.
References
Picture reference: Parkinsons Disease. National Institue of Environmental Health Sciences.
Available from: http://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/conditions/parkinson/