Peripheral Nervous System: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The Peripheral Nervous System (or PNS) is the name given to the parts of the nervous system not found within the [[ | The Peripheral Nervous System (or PNS) is the name given to the parts of the nervous system not found within the [[Central nervous system|central nervous system]] (CNS), ie. not found within the [[Brain|brain]] or spinal cord (see diagram of human CNS and PNS below). It is composed of several bundles of [[Neuron|neurons]] called nerves which connect the various sensors throughout the body to the CNS (afferent neurons) and the CNS to the various effectors throught the body (efferent neurons). As these neurones are not protected by the bone of the [[Skull|skull]] or spine, or the blood-brain barrier, they are far more suseptible to both physical and chemical damage. <ref>Hill R., Wyse G., Anderson M. (2008) Animal Physiology, 2nd edition, Sunderland Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates. (page 372)</ref><ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peripheral_nervous_system</ref> | ||
[[Image:Nervous system diagram.png]]<ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Nervous_system_diagram.png</ref>The Human Nervous System. Blue is PNS while red is CNS. | [[Image:Nervous system diagram.png]]<ref>http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Nervous_system_diagram.png</ref>The Human Nervous System. Blue is PNS while red is CNS. | ||
Revision as of 18:23, 1 December 2011
The Peripheral Nervous System (or PNS) is the name given to the parts of the nervous system not found within the central nervous system (CNS), ie. not found within the brain or spinal cord (see diagram of human CNS and PNS below). It is composed of several bundles of neurons called nerves which connect the various sensors throughout the body to the CNS (afferent neurons) and the CNS to the various effectors throught the body (efferent neurons). As these neurones are not protected by the bone of the skull or spine, or the blood-brain barrier, they are far more suseptible to both physical and chemical damage. [1][2]
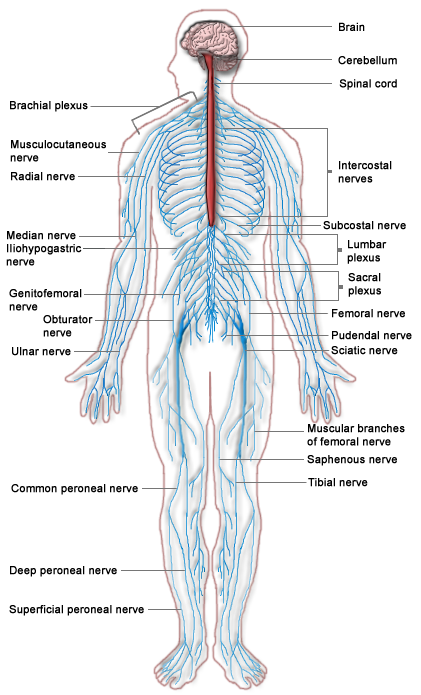 [3]The Human Nervous System. Blue is PNS while red is CNS.
[3]The Human Nervous System. Blue is PNS while red is CNS.
References
- ↑ Hill R., Wyse G., Anderson M. (2008) Animal Physiology, 2nd edition, Sunderland Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates. (page 372)
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peripheral_nervous_system
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Nervous_system_diagram.png