Bone
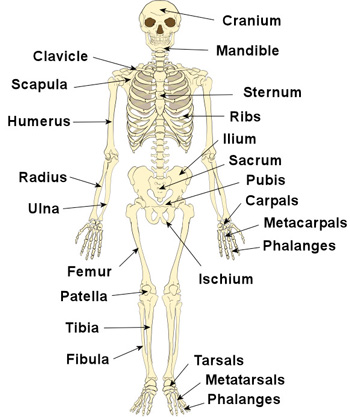
There are two-hundred and six bones in the adult human body[1][2]. Children have more bones (270 as an infant), as bones in the skull are separate and have not yet fused together (ossification). These bones make up the skeletal system which helps support the body and aid in movement. Bones are constantly being remodelled. In the human skeleton, there are two main types of bone: long bones and flat bones[3], and three others - short, irregular and sesmoif. Long bones, such as the femur (thigh bone), are made up of a long shaft and two ends. the shaft contains a cavity filled with bone marrow. They provide strength, structure and mobility. Flat bones are mainly found in the skull, ilium, sternum and ribcage and are made of two thin layers of compact bone, with a layer of cancellous bone in between them[4].
References
- ↑ Denise M. Covert, R.N.. (2011). How Many Bones Are There in the Human Body?. Available: http://howmanyarethere.net/how-many-bones-are-there-in-the-human-body/. Last accessed 23rd Oct 2012
- ↑ TeachPE. 2016 [cited 04/12/2016]; Available from:fckLRhttp://www.teachpe.com/anatomy/skeleton.php
- ↑ Biology for the Medical Sciences, P. Bradley and J. Calvert
- ↑ http://www.teachpe.com/anatomy/types_of_bones.php (Last accessed 25th Oct 2012)