Monocyte
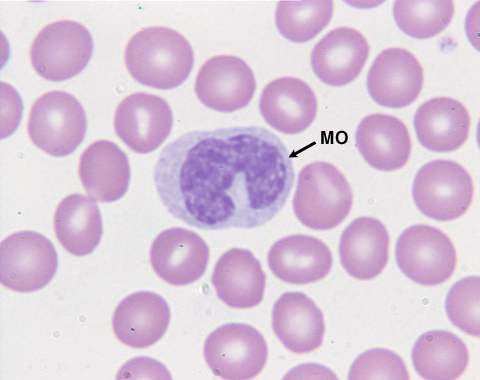
Monocytes are a type of white blood cell, they range from 13 μm to 25 μm in diameter and are distinguishable from their kidney-shaped nucleus. Monocytes originate from the common myeloid progenitor which differentiates to become a granulocyte and then a monocyte. Monocytes are a phagocytic cell found in the blood, they enter tissues and differentiate to form phagocytic Macrophages[1]. Once matured monocytes are often found in the lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, and loose connective tissue [2][3]. One key role monocytes play in immunity is the ability to differentiate into 2 different cell types - dendritic cells & tissue macrophages[4].
References:
- ↑ Murphy, K. (2012) Janeway's Immunobiology, 8th Edition, New York: Garland Science. p.4-6
- ↑ Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary, 2012 found at: https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/monocyte
- ↑ Photograph of monocyte available from: http://imgarcade.com/monocyte.html
- ↑ https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-are-monocytes-2252110