Tropomyosin
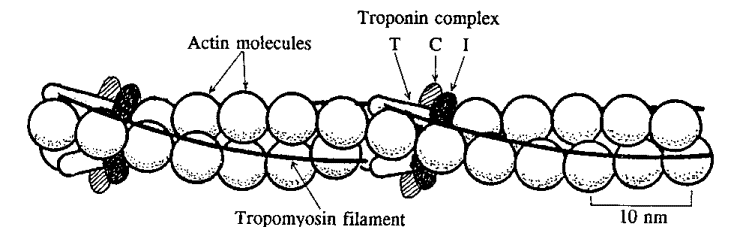
According to B. Alberts[1] tropomyosin is an elongated protein, which stabilizes actin filaments by binding to seven adjacent actin subunits, thus preventing it from interacting with other proteins [2]. Tropomyosin, along with troponin play an important role in regulation of muscle contraction [3]. As tropomyosin binds to actin it follows its helical structure [4]. Fig.1
This figure describes the relative position of accesory proteins and actin in a thin filament. Troponin complex is bound to actin and tropomyosin, which lies in the groove of the actin helix.
References
- ↑ B. Alberts, Molecular Biology of the Cell, Garland Science, 5th edition, 2008
- ↑ B. Alberts, Molecular Biology of the Cell, Garland Science, 5th edition, 2008
- ↑ R.D Keynes, D.J Aidley, Nerve and Muscle, 3rd edition, Cambridge University Press, 2001
- ↑ B.Alberts, Molecular Biology of the Cell, 5th edition, Garland Science, 2008
- ↑ San Diego State University (unknown), Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function, http://www-rohan.sdsu.edu/course/ens304/public_html/section1/Muscle.htm