Phosphodiester bond
The phosphodiester bond links two pentose sugars to a phosphate groups by strong, covalent ester bonds. The formation of these bonds is a condensation reaction in which water is lost. This bond is a key structural feature of the backbone of DNA and RNA and links the 3’ carbon of one nucleotide to the 5’ carbon of another to produce the strands of DNA and RNA.
Phosphodiester Bond Formation
In phosphodiester formation, the 1’ and 2’ OH groups of the phosphate molecule bind to the 3’ and 5’ carbons of the two independent pentose sugars. These are two condensation reactions so produce two molecules of water. The phosphate is then bonded to the sugars by two ester bonds so is called a phosphodiester bond.
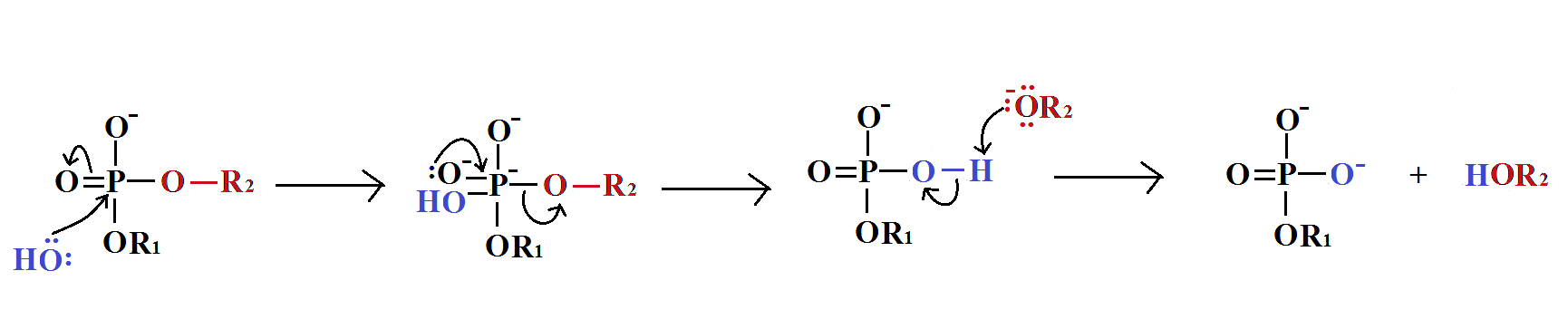
Phosphodiester Bond Hydrolysis
In phosphodiester hydrolysis, water dissociated into H+ and OH-. The OH- acts as the nucleophile in the nucleophilic substitution reaction of hydrolysis. The reaction is catalyses by phosphodiesterase.
The mechanism of this reaction is given below.