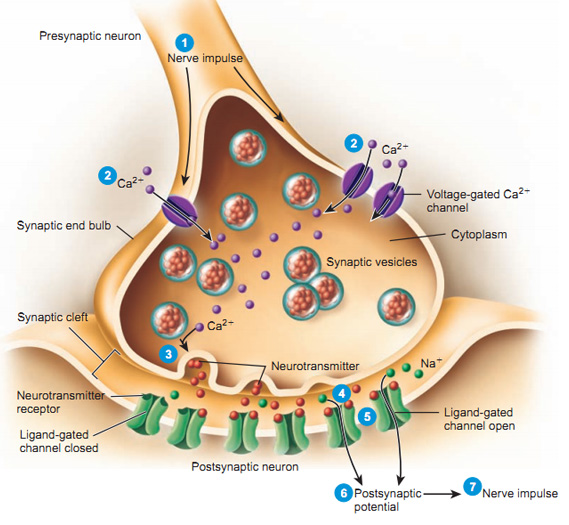
Synaptic transmission
Electrical transmission occurs when an action potential reaches an axon termina, this depolarises the pre synaptic membrane. Voltage gated ca2+ channels on the pre synaptic membrane, open in response to this depolarisation of the pre synaptic membrane. Ca2+ enters the axon terminal, down a concentration gradient through these open channels. This, causes the vesicles containing the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, to migrate towards the pre synaptic membrane. These vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane, and acetylcholine molecules are released into the synaptic clef, by the process of exocytosis. Acetylcholine molecules diffuse across the synaptic clef, and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. The binding of acetylcholine causes ligand gated Na+ channels to open, Na+ rushes into the postsynaptic membrane depolarising it to the threshold potential, therefore setting off an action potential.
Antranik (2012) Synaptic Transmission by Somatic Motorneurons, [Online], Available: http://antranik.org/synaptic-transmission-by-somatic-motorneurons/ accessed [27 Nov 2013].
Figure.1