Relay neuron
A relay neuron (also known as an interneuron) passes signals between neurons. Relay neurones are only found in the brain, visual system and spinal cord acting to relay signals. They recieve a signal from one neuron and then transfer the signal to another interneuron resulting in the signal being passed to a motor neurone thus driving the reaction to the stimulus. [1]
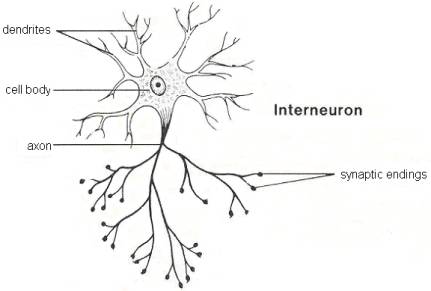
These can be differentiated from other neurones by observing their short dendrites and either long or short axons..[2]
References
- ↑ Becker W., Hardin J., Bertoni G., and Kleinsmith L. (2012) Becker’s World Of The Cell, 8th Edition, San Francisco: Pearson Education. Page 365
- ↑ The structure and function of sensory, relay and motor neurons. [Internet]. Psychology Hub. 2017 [cited 3 December 2017]. Available from: https://psychologyhub.co.uk/the-structure-and-function-of-sensory-relay-and-motor-neurons/