Semi-conservative replication: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
Added meaning of semi-conservative |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
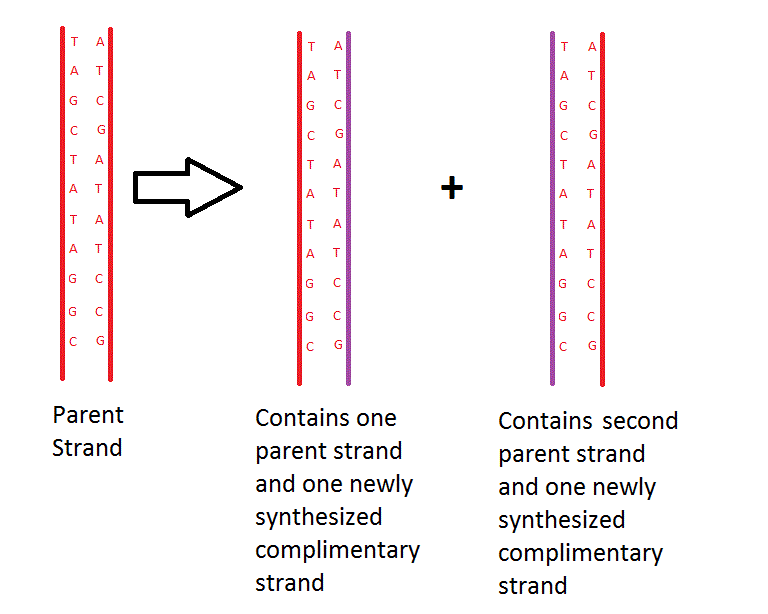
Semi-conservative replication is the mechanism by which [[DNA|DNA]] replicates in [[Cell|cells]]. | Semi-conservative replication is the mechanism by which [[DNA|DNA]] replicates in [[Cell|cells]]. The parent strand splits in two and uses itself as a template to form a second [[Complimentary strand|complimentary strand]]. Together the template strand and the complimentary strand bond together to form a new double strand of DNA. One parent double strand of DNA will thus become two daughter double strands of DNA <ref>Hartl, D and Jones, E (2009). Genetics- Analysis of genes and genomes. 7th ed. Sudbury: Jones and Bartlett publishers, Inc. 192.</ref>. | ||
The term "semi-conservative" refers to the fact that each of daughter double helix contains one conserved strand from the parent DNA, as well as one newly synthesised strand. | |||
<br>[[Image:Semi-conservative replication.gif]] | <br>[[Image:Semi-conservative replication.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 19:08, 9 November 2012
Semi-conservative replication is the mechanism by which DNA replicates in cells. The parent strand splits in two and uses itself as a template to form a second complimentary strand. Together the template strand and the complimentary strand bond together to form a new double strand of DNA. One parent double strand of DNA will thus become two daughter double strands of DNA [1].
The term "semi-conservative" refers to the fact that each of daughter double helix contains one conserved strand from the parent DNA, as well as one newly synthesised strand.
References
- ↑ Hartl, D and Jones, E (2009). Genetics- Analysis of genes and genomes. 7th ed. Sudbury: Jones and Bartlett publishers, Inc. 192.