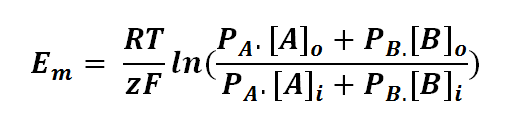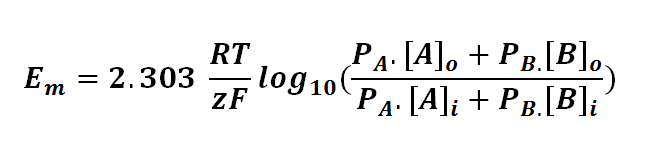Goldman equation: Difference between revisions
Created page with ''''Goldman equation''' is an equation used to calculate the electrical equilibium potential across the cell's membrane in the presence of more than one ions taking into account t…' |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Goldman equation''' is an equation used to calculate the electrical equilibium potential across the cell's membrane in the presence of more than one ions taking into account the selectivity of membrane's permeability. It is derived from the Nernst equation. <br> | '''Goldman equation''' is an equation used to calculate the electrical equilibium potential across the [[Cell_membrane|cell's membrane]] in the presence of more than one ions taking into account the selectivity of membrane's permeability. It is derived from the [[Nernst_Equation|Nernst equation]]. <br> | ||
== Equation<br> == | == Equation<br> == | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
The Goldman equation can be expressed as follows:<br> | The Goldman equation can be expressed as follows:<br> | ||
[[Image:Goldman eqn1.png|412x105px|Goldman eqn1.png]]<br> | |||
[[Image: | |||
or<br> | or<br> | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Goldman eqn2.png|520x124px|Goldman eqn2.png]]<br> | ||
<br> | |||
where<br> | where<br> | ||
< | E<sub>m</sub> is the potential difference of an ion between membranes | ||
R is the universal gas constant; R = 8.314471 J mol-1 | |||
T is the thermodynamics temperature, in Kelvin; 0 K = -273.15oC | |||
z is the number of moles of electrons transferred between membranes (defined by the valency of ion) | |||
F is the Faraday's constant; F = 96,485.3415 C mol-1 | |||
P<sub>A or B </sub>is the permeability of the membrane to a particular ion (A or B) | |||
P<sub>A or B </sub>is the permeability of the membrane to a particular ion (A or B) | |||
[A or B]<sub>o</sub> is the concentration of ion outside the membrane <br> | [A or B]<sub>o</sub> is the concentration of ion outside the membrane <br> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 34: | ||
== References<br> == | == References<br> == | ||
== External Links == | |||
*[http://www.nernstgoldman.physiology.arizona.edu/ The Nernst/Goldman Equation Simulator] | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Latest revision as of 10:20, 25 October 2013
Goldman equation is an equation used to calculate the electrical equilibium potential across the cell's membrane in the presence of more than one ions taking into account the selectivity of membrane's permeability. It is derived from the Nernst equation.
Equation
The Goldman equation can be expressed as follows:
or
where
Em is the potential difference of an ion between membranes
R is the universal gas constant; R = 8.314471 J mol-1
T is the thermodynamics temperature, in Kelvin; 0 K = -273.15oC
z is the number of moles of electrons transferred between membranes (defined by the valency of ion)
F is the Faraday's constant; F = 96,485.3415 C mol-1
PA or B is the permeability of the membrane to a particular ion (A or B)
[A or B]o is the concentration of ion outside the membrane
[A or B]i is the concentration of ion inside the membrane
See also
References
External Links