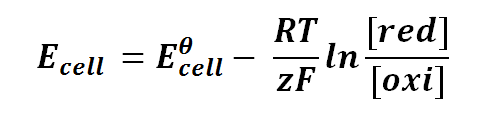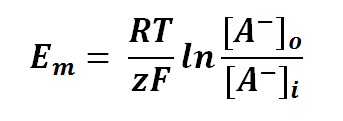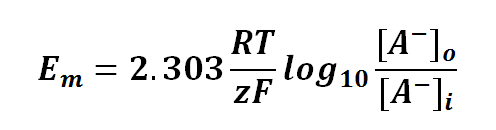Nernst Equation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
== Application == | == Application == | ||
=== Ussing Study of Frog Skin === | === Ussing Study of Frog Skin === | ||
In biochemistry, Nernst equation can be used to calculate the potential difference of ion between membranes. Hans H. Ussing, a Danish scientist, used a frog skin to measure the potential difference of sodium and potassium ions across the membranes with his famous invention, the Ussing chamber. | |||
Revision as of 21:48, 14 November 2010
Nernst Equation is an equation used to calculate the electrical potential of a chemical reaction. In its equilibrium state, the Nernst equation should be zero. It also shows the direct relation between energy or potential of a cell and its participating ions. The equation is proposed by a German chemist, Walther H. Nernst (1864-1941).
Equation
Nernst equation can be expressed as follows:
where
Ecell is the half-cell potential difference
Eθcell is the standard half-cell potential
R is the universal gas constant; R = 8.314471 J K-1 mol-1
T is the thermodynamics temperature, in Kelvin; 0 K = -273.15oC
z is the number of moles of electrons transferred between cells (defined by the valency of ions)
F is the Faraday's constant; F = 96,485.3415 C mol-1
[red] is the concentration of ion that gained electrons (reduction)
[oxi] is the concentration of ion that lost electrons (oxidation)
Membrane Potential
Nernst equation is also can be used to calculate the potential of an ion across the membrane. For potential difference of a membrane, we can manipulate the Nernst Equation as follows:
or
where
Em is the potential difference of an ion between membranes
R is the universal gas constant; R = 8.314471 J mol-1
T is the thermodynamics temperature, in Kelvin; 0 K = -273.15oC
z is the number of moles of electrons transferred between membranes (defined by the valency of ion)
F is the Faraday's constant; F = 96,485.3415 C mol-1
[A-1] is the concentration of ion outside the membrane
[A-1] is the concentration of ion inside the membrane
Application
Ussing Study of Frog Skin
In biochemistry, Nernst equation can be used to calculate the potential difference of ion between membranes. Hans H. Ussing, a Danish scientist, used a frog skin to measure the potential difference of sodium and potassium ions across the membranes with his famous invention, the Ussing chamber.