G-protein Coupled Receptor: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
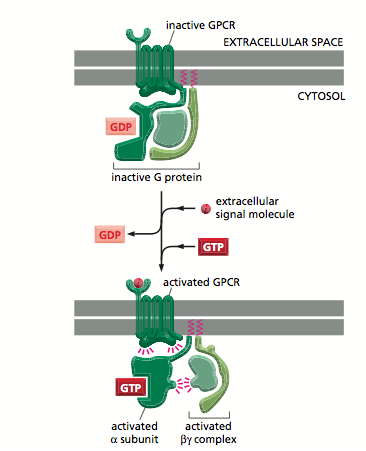
Trimeric G Proteins are made up of alpha beta and gamma subunits<ref>Alberts.B Johnson.A Lewis Raff.J Roberts.K Walter.P Molecular Biology of the cell 5th edition Garland science page 892</ref>. Alpha subunits have inate [[GTPase|GTPase]] activity- They bind to GDP in their resting state<ref>Alberts.B Johnson.A Lewis Raff.J Roberts.K Walter.P Molecular Biology of the cell 5th edition Garland science page 896</ref>. They are attached to the receptor at resting state in contrast to monomeric G proteins<ref>Alberts.B Johnson.A Lewis Raff.J Roberts.K Walter.P Molecular Biology of the cell 5th edition Garland science page number 892-896</ref><br> | Trimeric G Proteins are made up of alpha beta and gamma subunits<ref>Alberts.B Johnson.A Lewis Raff.J Roberts.K Walter.P Molecular Biology of the cell 5th edition Garland science page 892</ref>. Alpha subunits have inate [[GTPase|GTPase]] activity- They bind to GDP in their resting state<ref>Alberts.B Johnson.A Lewis Raff.J Roberts.K Walter.P Molecular Biology of the cell 5th edition Garland science page 896</ref>. They are attached to the receptor at resting state in contrast to monomeric G proteins<ref>Alberts.B Johnson.A Lewis Raff.J Roberts.K Walter.P Molecular Biology of the cell 5th edition Garland science page number 892-896</ref><br> | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Screen Shot 2013-10-20 at 17.30.44.png]] | ||
figure 1: showing active and inactive G-protein | figure 1: showing active and inactive G-protein | ||
= References = | = References = | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 16:48, 20 October 2013
The G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) is a seven transmembrane spanning receptor that interacts with G-protein in the process of cell signalling. It constitutes along with ion-channel-coupled receptors and enzyme-coupled receptors a major class of cell surface-receptor [1].
Classification
Over 800 G-protein-coupled receptors have been identified (more than half of them being olfactory receptors) and phylogenetic studies carried out [2]. From these studies the GPCRs can be classified in five main families:
- The rhodopsin receptor family of receptors structurally similar to rhodopsin, contains the largest number of receptors, including all the olfactory ones. Other members of this family include the adrenergic receptors, muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs), glycoprotein-hormone receptors, serotonine receptors (except the ionotropic 5-HT3 receptor), prostaglandin receptors, thrombin receptor, etc.
- The glutamate receptor family includes the glutamate metabotropic receptors, and GABAB receptors.
- The secetrin receptor family with the receptor for the peptide hormone secretine as a prototype, it also includes the receptor for glucagon, calcitonin and parathyroid hormone.
- The adhesion receptor family characterized by the presence of motifs in the N-terminus that are likely to be related to cell adhesion.
- The Frizzled/Taste2 receptor family includes receptors important for development (frizzled branch) and the taste receptors (TAS2 branch).
Structure
Along with the seven transmembrane core structure, the G Protein Coupled Receptor often have large receptor domains in the N-terminus on the extracellular side of the plasma membrane. Binding of a signal molecule to this receptor domain (or indeed the extracellular part of the transmembrane domains) cause a conformational change in the transmembrane domain and intracellular C-terminus. This triggers the action of a G-protein which binds guanyl nucleotides [3].
G proteins are of two types- Monomeric and Trimeric G proteins respectively [4].
Trimeric G Proteins are made up of alpha beta and gamma subunits[5]. Alpha subunits have inate GTPase activity- They bind to GDP in their resting state[6]. They are attached to the receptor at resting state in contrast to monomeric G proteins[7]
figure 1: showing active and inactive G-protein
References
- ↑ Alberts, et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 5th ed. Garland Science. 2008
- ↑ Fredriksson R, Lagerström MC, Lundin LG, Schiöth HB. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints.Mol Pharmacol. 2003 Jun;63(6):1256-72.
- ↑ Berg, JM, Biochemistry, 6th Edition (2007), WH Freeman and Company, New York
- ↑ Alberts.B Johnson.A Lewis Raff.J Roberts.K Walter.P Molecular Biology of the cell 5th edition Garland science page number 892-893
- ↑ Alberts.B Johnson.A Lewis Raff.J Roberts.K Walter.P Molecular Biology of the cell 5th edition Garland science page 892
- ↑ Alberts.B Johnson.A Lewis Raff.J Roberts.K Walter.P Molecular Biology of the cell 5th edition Garland science page 896
- ↑ Alberts.B Johnson.A Lewis Raff.J Roberts.K Walter.P Molecular Biology of the cell 5th edition Garland science page number 892-896