Glutamine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
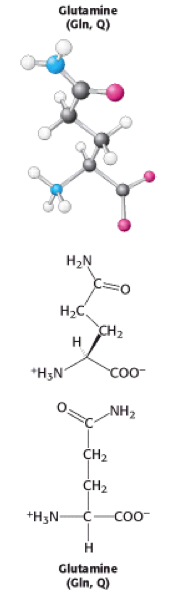
Glutamine is one of the 20 naturally occuring [[Amino acids|amino acids]]. It can be abbreviated to three letters: Gln or one letter: Q. It is a [[Polar|polar]] molecule meaning that it has an [[Enzyme|enzymatic]] role and can bind [[Ligand|ligands]] and other [[DNA|DNA]]. [[ | [[Image:Glutamine.png]] | ||
Glutamine is one of the 20 naturally occuring [[Amino acids|amino acids]]. It can be abbreviated to three letters: Gln or one letter: Q. It is a [[Polar|polar]] molecule meaning that it has an [[Enzyme|enzymatic]] role and can bind [[Ligand|ligands]] and other [[DNA|DNA]]. [[Polar amino acids|Polar amino acids]] are found buried in a [[Protein|protein]] and can be [[Hydrogen bonds|hydrogen-bonded]] to other [[Polar amino acids|polar amino acids]] or to the [[Polypeptide|polypeptide]] backbone <ref>Molecular biology of the cell, Alberts, 5th edition, chapter 3, page 126-129.</ref>. | |||
=== References === | === References === | ||
< | Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.<br> | ||
Revision as of 14:44, 29 November 2013
Glutamine is one of the 20 naturally occuring amino acids. It can be abbreviated to three letters: Gln or one letter: Q. It is a polar molecule meaning that it has an enzymatic role and can bind ligands and other DNA. Polar amino acids are found buried in a protein and can be hydrogen-bonded to other polar amino acids or to the polypeptide backbone [1].
References
Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.
- ↑ Molecular biology of the cell, Alberts, 5th edition, chapter 3, page 126-129.