Chromosome: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A chromosome is the name given to the structure that holds an organisms [[DNA|DNA]], either all or just part of it. Both plant and animal chromosomes become visible when [[Mitosis|mitosis]] or [[Meiosis|meiosis]] occur, they become much more condensed. | A chromosome is the name given to the structure that holds an organisms [[DNA|DNA]], either all or just part of it. Both plant and animal chromosomes become visible when [[Mitosis|mitosis]] or [[Meiosis|meiosis]] occur, they become much more condensed. | ||
In most cases bacterial chromosomes are often circular and not linear, as found in humans <ref>Molecular Biolody of the cell fifth edition, 2008</ref>. | In most cases bacterial chromosomes are often circular and not linear, as found in humans <ref>Molecular Biolody of the cell fifth edition, 2008</ref>. | ||
=== Structure of Chromosome: === | |||
1. Each chromosome compose of two identical sister chromatids. | 1. Each chromosome compose of two identical sister chromatids. | ||
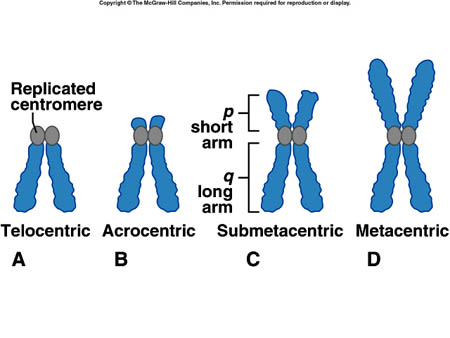
[[Image: | [[Image:Sister chromatids.jpg|182x161px|Sister chromatids.jpg]]<br> 2. The sister chromatids are hold on the centromere. [[Centromere|Centromere]] in the human chromosome doesn't have any distinct sequence, it is just a large array of repeated sequence.<br> The position of [[Centromere|centromere]] determine the type of chromosome. | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Tp11 02.jpg|335x269px|Tp11 02.jpg]] | ||
3. At the end of each chromosome also contain[[Telomere|telomere]], that is used to protect the chromosome from annealing with sister chromatids.<br>Also is used to distinguish the real end of chromosome from the end of chromosome caused by damaged; in addition, it is also used to solve end replication problem. | 3. At the end of each chromosome also contain [[Telomere|telomere]], that is used to protect the chromosome from annealing with sister [[chromatids|chromatids]].<br>Also is used to distinguish the real end of chromosome from the end of chromosome caused by damaged; in addition, it is also used to solve end replication problem. | ||
=== References === | === References === | ||
<references /><br> | <references /><br> | ||
Revision as of 18:33, 29 November 2011
A chromosome is the name given to the structure that holds an organisms DNA, either all or just part of it. Both plant and animal chromosomes become visible when mitosis or meiosis occur, they become much more condensed.
In most cases bacterial chromosomes are often circular and not linear, as found in humans [1].
Structure of Chromosome:
1. Each chromosome compose of two identical sister chromatids.

2. The sister chromatids are hold on the centromere. Centromere in the human chromosome doesn't have any distinct sequence, it is just a large array of repeated sequence.
The position of centromere determine the type of chromosome.
3. At the end of each chromosome also contain telomere, that is used to protect the chromosome from annealing with sister chromatids.
Also is used to distinguish the real end of chromosome from the end of chromosome caused by damaged; in addition, it is also used to solve end replication problem.
References
- ↑ Molecular Biolody of the cell fifth edition, 2008