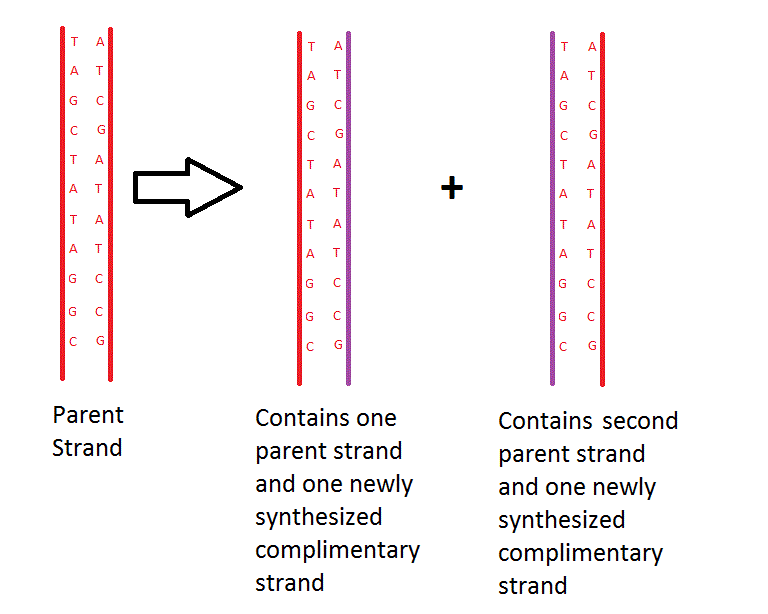
Semi-conservative replication
Semi-conservative replication is the mechanism by which DNA replicates in cells. The parent strand splits in two and uses itself as a template to form a second complimentary strand. Together the template strand and the complimentary strand bond together to form a new double strand of DNA. One parent double strand of DNA will thus become two daughter double strands of DNA [1].
References
- ↑ Hartl, D and Jones, E (2009). Genetics- Analysis of genes and genomes. 7th ed. Sudbury: Jones and Bartlett publishers, Inc. 192.