Transduction
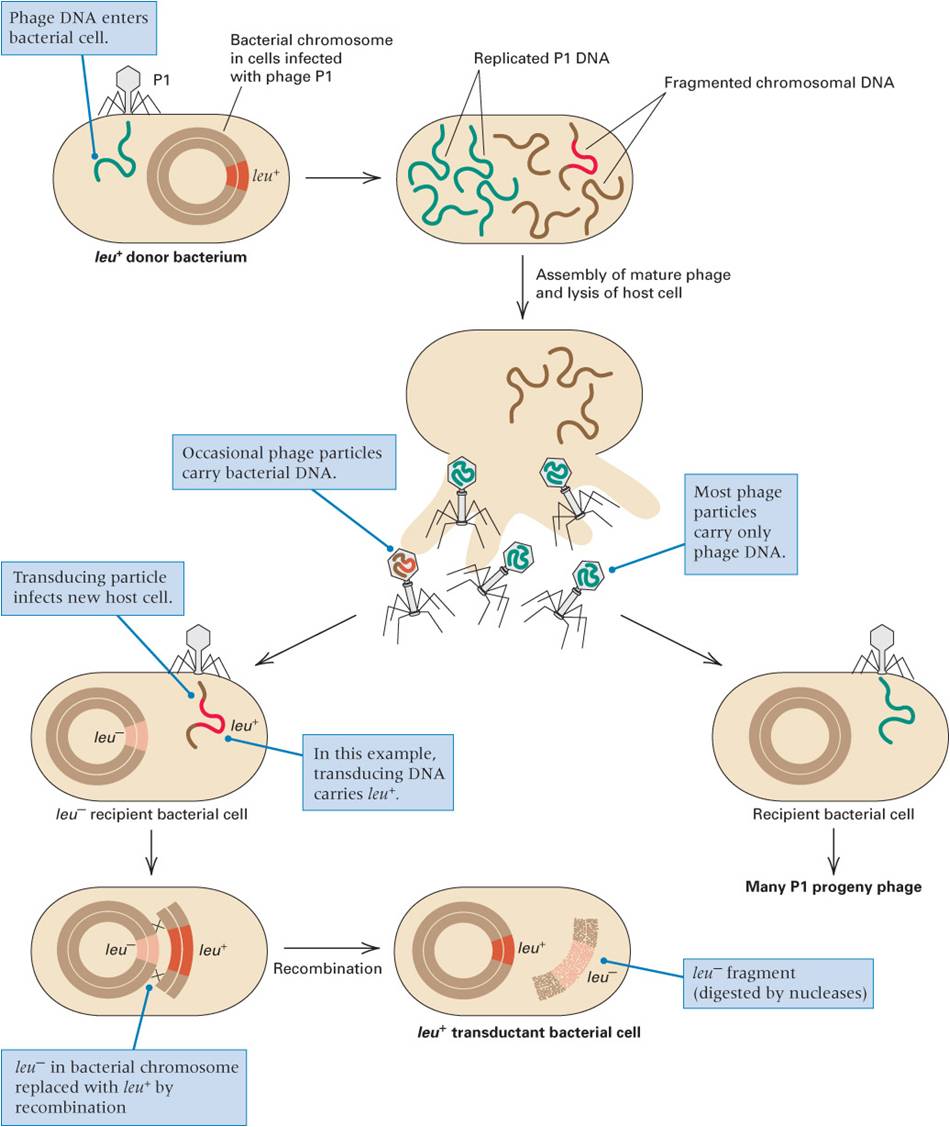
Transduction is where DNA is transferred from one bacterial cell to another via a transducing phage.
The generalised process by which this is done is a transducing phage lands on the surface of a bacterium and injects the phage into the bacterium. The infects the bacterium and causes the chromosome to fragment and the phage DNA can be replicated many times and packaged into phages creating mature transducing phages. Lysis of the cell occurs and the transducing phages are released, and can then go on to attach to other host cells [1].
References
- ↑ Hartl D. and Ruvolo M., (2012), Genetics: Analysis of Genes & Genomes, 8th edition, Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Chapter 9.