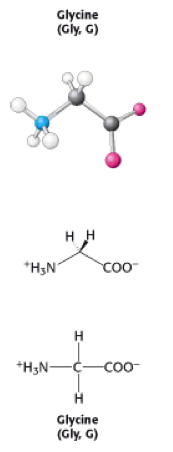
Glycine
Glycine is one of the 20 amino acids. It's three letter code is Gly, and it's single letter code is G. It is the simplest amino acid, with a hydrogen atom as a side chain - this means glycine is the only amino acid which does not have a chiral carbon atom [1], so it does not form stereoisomers therefore will not have L or D configurations.
Glycine has a function outside of the cell. It plays a vital role in the central nervous system as is acts as a neurotransmitter in chemical synapses [2].
Glycine has two hydrogens attatched to the alpha carbon and is found in flexible areas of proteins due to its short side chain [3].
References
- ↑ Priv.-Doz. B. Kirste. (01-23-1998). Glycine. Available: http://www.chemie.fu-berlin.de/chemistry/bio/aminoacid/glycin_en.html. Last accessed 23-11-2010.
- ↑ Molecular biology of the cell,4th edition, 2002, Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson , Julian Lewis, Martin Raff , Keith Roberts and Peter Walter. Page 764
- ↑ http://www.acnp.org/g4/gn401000008/default.htm
- ↑ Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.