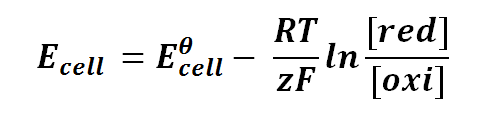Nernst Equation
Nernst Equation
Nernst Equation is an equation used to calculate the electrical potential of a chemical reaction. In its equilibrium state, the Nernst equation should be zero. It also shows the direct relation between energy or potential of a cell and its participating ions. The equation is proposed by a German chemist, Walther H. Nernst (1864-1941).
Equation
Nernst equation can be expressed as follows:
where
Ecell is the half-cell potential difference
Eθcell is the standard half-cell potential
R is the universal gas constant; R = 8.314471 J K-1 Mol-1