Cat eye syndrome
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
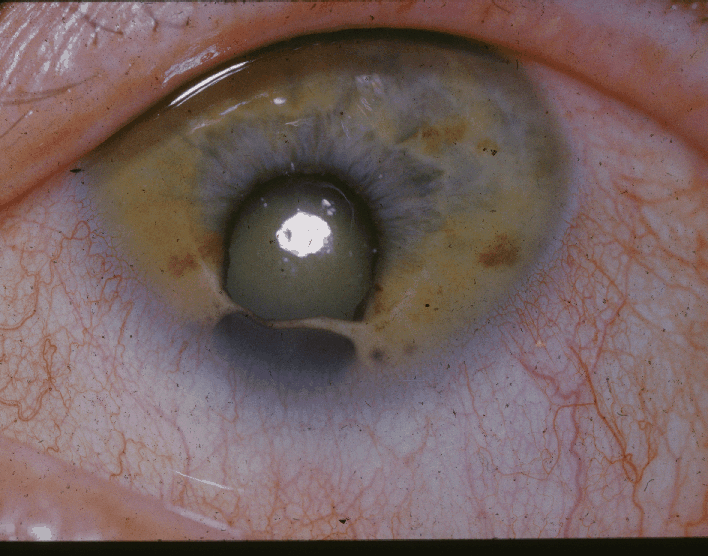
Cat eye syndrome (CES) or Schmid–Fraccaro syndrome is an uncommon chromosomal disorder that involves a trisomy or tetrasomy of part of chromosome 22. The term of 'cat eye' is derived from the vertical, cat-like pupils that people with the syndrome often present. Symptoms associated with this syndrome are very variable and can affect almost every organ. Some of the most common features are:[1][2]
- Anal atresia
- Ear tags
- Widely set eyes
- Strabismus (squinting)
- Heart defects
- Kidney malformations
Patients suffering CES can present normal intelligence. Nevertheless, some individuals can present mental retardation, rarely cases of several retardion are reported. [3]
Approximately 1-9 out of 100 000 persons have this rare disorder. [4]