Watson-Crick base pairs
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
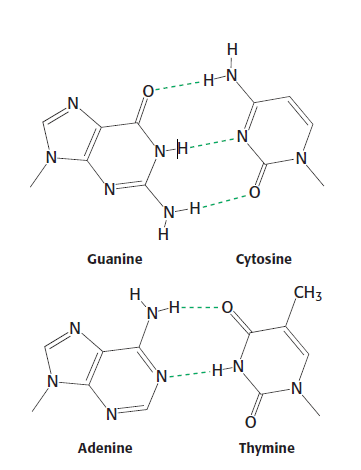
[1]Watson-Crick base pairs is a specific complementary base pairs that base A is always paired with base T while base G is always paired with base C. These base pairs were introduced by James Watson and Francis Crick. In Watson-Crick base pairs, the number of hydrogen bonds formed between A and T are 2 while there are 3 formed between base G and C[2]. Cytosine and Thymine are pyrimidine compounds and Guanine and Adenine are purine compounds. The purine compunds are larger than the pyrimidines as the 6-membered ring has an extra 5-membered ring fused to it[3].
References
- ↑ Berg, J, Stryer,L ,Tymoczko J,2012, Biochemistry, 7th edition. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York. Pg. 114, Figure 4.12.
- ↑ Berg, J, Stryer,L ,Tymoczko J,2012, Biochemistry, 7th edition. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York. Pg. 114
- ↑ Alberts et al. Molecular biology of the cell, fifth edition, 2007. Page 61