Leucine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
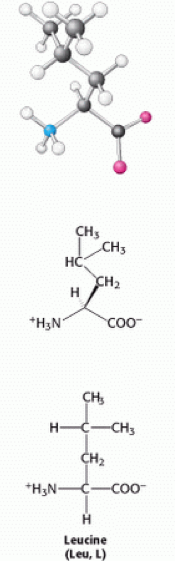
Leucine is an [[Amino acids|amino acid]] which has the [[Single letter amino acid codes|single letter amino acid code]] L, and the 3 letter code Leu. It is a hydrophobic and [[Non-polar amino acid|non-polar]] amino acid. It is coded for by the [[Nucleotide|nucleotide]] base sequences: CUU, CUA, CUC and CUG <ref>https://www.dna20.com/codontablewheel.php</ref><ref>Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., & Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.</ref>. | Leucine is an [[Amino acids|amino acid]] which has the [[Single letter amino acid codes|single letter amino acid code]] L, and the 3 letter code Leu. It is a hydrophobic and [[Non-polar amino acid|non-polar]] amino acid. It is coded for by the [[Nucleotide|nucleotide]] base sequences: CUU, CUA, CUC and CUG <ref>https://www.dna20.com/codontablewheel.php</ref><ref>Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., &amp;amp; Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.</ref>. | ||
[[Image:Leucine.png]] | [[Image:Leucine.png]] | ||
=== Protein Metabolism === | |||
Leucine is one of the three [[Essential amino acids]] that makes up a group called the [[Branched chain amino acids]] ( or [[BCAAs]]). These BCAAs have ben described as [[Hormone|hormone]] [[Secretagogues]], as well as having roles to play in intracellular signalling - affecting gene [[Transcription|transcription and]] [[Translation|translation]]. <ref>Sreekumaran, N. Short, Kevin R. (2005) The Journal of Nutrition, vol. 135, no. 6, p. 15475-15525.</ref> | |||
Leucine is the only amino acid with the unique ability to stimulate muscle protein synthesis through the interaction with [[Mammalian target of rapamycin|mammalian target of rapamycin]] (mTOR). <ref>Gran, P. Cameron-Smith, D. (2011) BioMed Central, doi: 10.1186/1472-6793-11-10</ref> This has led to a lot of research which may indicate that leucine rich diets may prevent muscle wastage when ageing or engaging in high intensity sport, and may even help in repair of muscle following injury. <ref>Pereira, Marcelo G. et al. (2014) Nutrients. 6 (10), 3981-4001</ref><ref>Luiking, Yvette C. et al, (2014) Nutritional Journal, 13: 9, 10.1186/1475-2891-13-9</ref> | |||
=== References: === | === References: === | ||
<references /><br> | <references /><br> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:45, 19 October 2015
Leucine is an amino acid which has the single letter amino acid code L, and the 3 letter code Leu. It is a hydrophobic and non-polar amino acid. It is coded for by the nucleotide base sequences: CUU, CUA, CUC and CUG [1][2].
Protein Metabolism
Leucine is one of the three Essential amino acids that makes up a group called the Branched chain amino acids ( or BCAAs). These BCAAs have ben described as hormone Secretagogues, as well as having roles to play in intracellular signalling - affecting gene transcription and translation. [3]
Leucine is the only amino acid with the unique ability to stimulate muscle protein synthesis through the interaction with mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). [4] This has led to a lot of research which may indicate that leucine rich diets may prevent muscle wastage when ageing or engaging in high intensity sport, and may even help in repair of muscle following injury. [5][6]
References:
- ↑ https://www.dna20.com/codontablewheel.php
- ↑ Berg, J. M., Tymoczko, J. L., &amp; Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman.
- ↑ Sreekumaran, N. Short, Kevin R. (2005) The Journal of Nutrition, vol. 135, no. 6, p. 15475-15525.
- ↑ Gran, P. Cameron-Smith, D. (2011) BioMed Central, doi: 10.1186/1472-6793-11-10
- ↑ Pereira, Marcelo G. et al. (2014) Nutrients. 6 (10), 3981-4001
- ↑ Luiking, Yvette C. et al, (2014) Nutritional Journal, 13: 9, 10.1186/1475-2891-13-9