Maltose: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with 'Maltose is a disaccharide. In maltose, two units of glucose are joined in a condensation reaction by an alpha-1,4 glycosidic linkage. Maltose is p…' |
No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
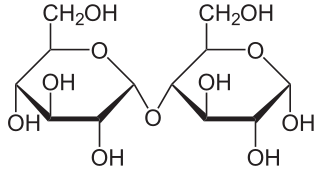
Maltose is a disaccharide. In maltose, two units of [[Glucose|glucose]] are joined in a condensation reaction by an [[ | Maltose is a [[Disaccharide|disaccharide]]. In maltose, two units of [[Glucose|glucose]] are joined in a [[Condensation Reaction|condensation reaction]] by an [[Glycosidic bond|alpha-1,4 glycosidic linkage]]. Maltose is produced by the [[Hydrolysis|hydrolysis]] of [[Starch|starch]] and can be hydrolysed to [[Glucose|glucose]] by the action of the [[Enzyme|enzyme]] [[Maltase|maltase]]<ref>'Biochemistry', Fifth Edition, (2002), Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko and Lubert Stryer, p.302</ref>. [[Image:Maltose.png|thumb|right]] | ||
=== References === | |||
<references /> | |||
Latest revision as of 10:08, 8 December 2018
Maltose is a disaccharide. In maltose, two units of glucose are joined in a condensation reaction by an alpha-1,4 glycosidic linkage. Maltose is produced by the hydrolysis of starch and can be hydrolysed to glucose by the action of the enzyme maltase[1].
References
- ↑ 'Biochemistry', Fifth Edition, (2002), Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko and Lubert Stryer, p.302