Ras signalling Pathway: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
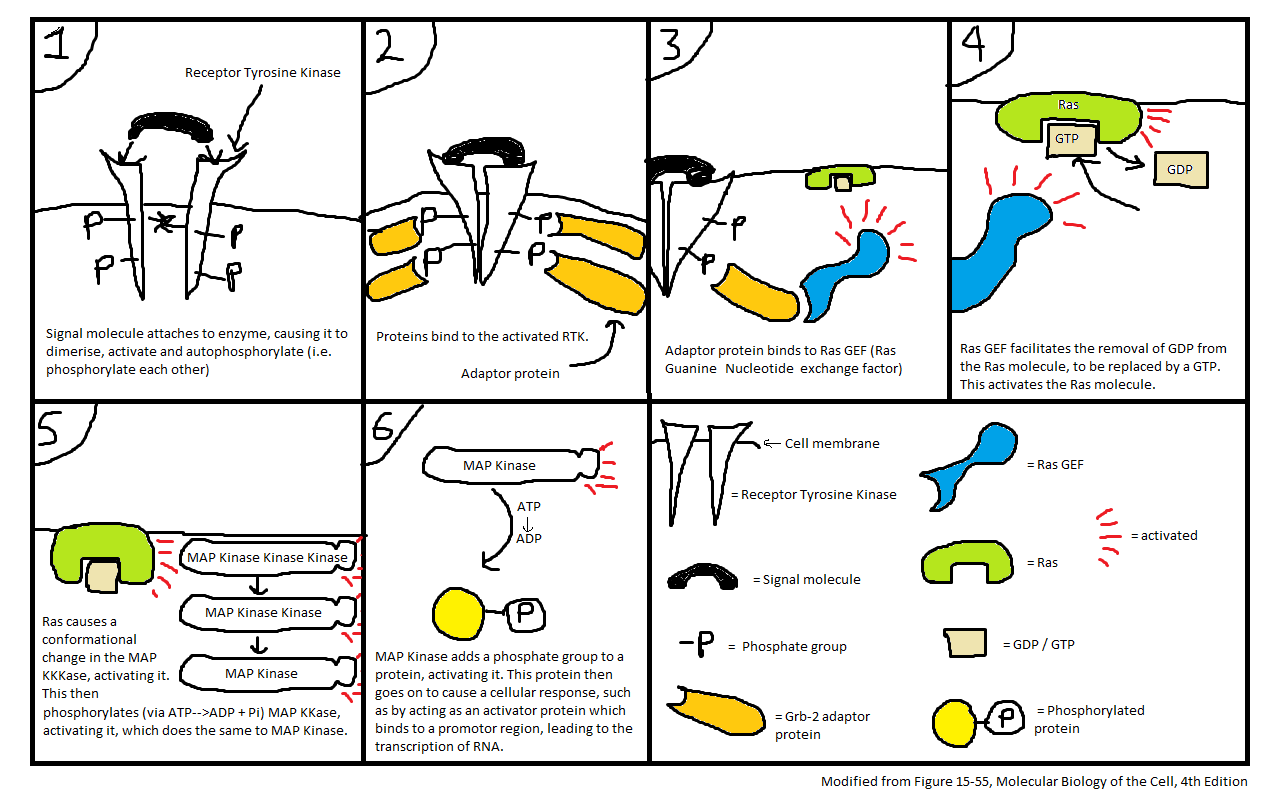
The Ras signalling pathway is the main pathway involved in the [[Cell signalling|transduction]] of [[Growth factors|growth factor]] signalling. It involves the dimerisation and [[Autophosphorylation|autophosphorylation]] of a [[Enzyme-coupled Receptor|receptor tyrosine kinase ]](RTK), located on the [[Cell membrane|cell membrane]], which is brought about | The Ras signalling pathway is the main pathway involved in the [[Cell signalling|transduction]] of [[Growth factors|growth factor]] signalling. It involves the dimerisation and [[Autophosphorylation|autophosphorylation]] of a [[Enzyme-coupled Receptor|receptor tyrosine kinase ]](RTK), located on the [[Cell membrane|cell membrane]], which is brought about by the binding of a [[Ligand|ligand]] (signalling molecule) to the receptor site on the RTK molecule. This triggers the binding of an [[Adaptor protein|adaptor protein]] ([[Grb-2|Grb-2]]) to the [[Phosphate|phosphate group on]] the RTK, and to that adaptor protein binds a Ras [[GEF|GEF]] molceule ([[Ras Guanine Nucleotide Exchange factor|Ras Guanine Nucleotide Exchange factor]]) which becomes activated. This molecule facilitates the removal of [[GDP|GDP]] from a nearby Ras [[Molecule|molecule]] (a [[Monomeric G-protein|monomeric G-protein]]), which is replaced by [[GTP|GTP]], and this results in the activation of the Ras. This activated Ras causes a conformational change in a nearby [[MAP Kinase Kinase Kinase|MAP Kinase Kinase Kinase]] resulting in the activation of the molecule. Via the conversion of [[ATP|ATP]] to [[ADP|ADP]], the [[MAP KKKase|MAP KKKase]] [[Phosphorylation|phosphorylates]] a MAP Kinase Kinase, which then phosphorylates a MAP Kinase. This enzyme then phosphorylates a protein, activating it, leading to a cellular response. | ||
[[Image:Enzyme Linked Receptors (Ras).png| | [[Image:Enzyme Linked Receptors (Ras).png|1040x656px|Enzyme Linked Receptors (Ras).png]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:55, 22 November 2011
The Ras signalling pathway is the main pathway involved in the transduction of growth factor signalling. It involves the dimerisation and autophosphorylation of a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), located on the cell membrane, which is brought about by the binding of a ligand (signalling molecule) to the receptor site on the RTK molecule. This triggers the binding of an adaptor protein (Grb-2) to the phosphate group on the RTK, and to that adaptor protein binds a Ras GEF molceule (Ras Guanine Nucleotide Exchange factor) which becomes activated. This molecule facilitates the removal of GDP from a nearby Ras molecule (a monomeric G-protein), which is replaced by GTP, and this results in the activation of the Ras. This activated Ras causes a conformational change in a nearby MAP Kinase Kinase Kinase resulting in the activation of the molecule. Via the conversion of ATP to ADP, the MAP KKKase phosphorylates a MAP Kinase Kinase, which then phosphorylates a MAP Kinase. This enzyme then phosphorylates a protein, activating it, leading to a cellular response.