Electron transfer chain: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Electron Transfer Chain''' The electron transfer chain is a series of protein complexes; [[NADH-Q oxioreductase|NADH-Q oxioreductase]], [[ | '''Electron Transfer Chain''' The electron transfer chain is a series of protein complexes; [[NADH-Q oxioreductase|NADH-Q oxioreductase]], [[Coenzyme_Q|Q-cytochrome C oxioreductase]], [[Cytochrome C oxidase|cytochrome C oxidase]] and [[ATP synthase|ATP synthase]]. These components contain certain redox centres, and electrons move to carriers with increasing electron affinity along the chain: [[Image:Electron transfer chain.jpg]] | ||
[Q is coenzyme Q, also known as ubiquinone, and carries electrons from NADH and FADH<sub>2</sub>. It is [[Hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] and diffuses rapidly in the inner mitochondrial membrane.]<br> | [Q is coenzyme Q, also known as ubiquinone, and carries electrons from NADH and FADH<sub>2</sub>. It is [[Hydrophobic|hydrophobic]] and diffuses rapidly in the inner mitochondrial membrane.]<br> | ||
• ''Complex I'' – [[NADH-Q oxioreductase|NADH-Q oxioreductase]]<br> o Transfer of two high-potential electrons from [[NADH|NADH]] to [[FMN|FMN]]<br> o Electrons from FMNH<sub>2</sub> transferred to a series of Fe-S clusters<br> o Electrons from [[Fe-S clusters|Fe-S clusters]] shuttled to [[Coenzyme Q|Coenzyme Q]]<br> o Net Effect – <br> 4H<sup>+</sup> pumped out of matrix into intermembrane space<br> 2 chemical H<sup>+</sup> removed from matrix<br> | • ''Complex I'' – [[NADH-Q oxioreductase|NADH-Q oxioreductase]]<br> o Transfer of two high-potential electrons from [[NADH|NADH]] to [[FMN|FMN]]<br> o Electrons from FMNH<sub>2</sub> transferred to a series of Fe-S clusters<br> o Electrons from [[Fe-S clusters|Fe-S clusters]] shuttled to [[Coenzyme Q|Coenzyme Q]]<br> o Net Effect – <br> 4H<sup>+</sup> pumped out of matrix into intermembrane space<br> 2 chemical H<sup>+</sup> removed from matrix<br> | ||
• ''Complex II'' – [[Succinate-Q reductase|Succinate-Q reductase]] complex<br> o [[Succinate dehydrogenase|Succinate dehydrogenase]] (in [[Citric Acid Cycle|Cirtic Acid Cycle]]) part of succinate-Q reductase complex<br> o Electrons from FADH<sub>2</sub> transferred to Fe-S clusters and then to Q<br> o ''Does not pump protons'' - therefore less ATP is formed by oxidation of FADH<sub>2</sub> than NADH<br> | • ''Complex II'' – [[Succinate-Q reductase|Succinate-Q reductase]] complex<br> o [[Succinate dehydrogenase|Succinate dehydrogenase]] (in [[Citric Acid Cycle|Cirtic Acid Cycle]]) part of succinate-Q reductase complex<br> o Electrons from FADH<sub>2</sub> transferred to Fe-S clusters and then to Q<br> o ''Does not pump protons'' - therefore less ATP is formed by oxidation of FADH<sub>2</sub> than NADH<br> | ||
• ''Complex III'' – [[Q-cytochrome C oxioreductase|Q-cytochrome C oxioreductase]]<br> o [[Cytochrome C|Cytochrome C]] is in all organisms with mitochondrial respiratory chains<br> o Small soluble protein containing C-type heme<br> o Carries one electron from Q-cytochrome C oxioreductase to cytochrome C oxidase<br> o Electrons transferred from QH<sub>2</sub> to oxidised cytochrome C (Cyt<sub>Cox</sub>) | • ''Complex III'' – [[Q-cytochrome C oxioreductase|Q-cytochrome C oxioreductase]]<br> o [[Cytochrome C|Cytochrome C]] is in all organisms with mitochondrial respiratory chains<br> o Small soluble protein containing C-type heme<br> o Carries one electron from Q-cytochrome C oxioreductase to cytochrome C oxidase<br> o Electrons transferred from QH<sub>2</sub> to oxidised cytochrome C (Cyt<sub>Cox</sub>) | ||
o Mechanism that couples electron transfer is known as the Q Cycle<br> | o Mechanism that couples electron transfer is known as the Q Cycle<br> | ||
• ''Complex IV'' – Cytochrome C Oxidase<br> o 4 electrons transferred from [[Cytochrome C|cytochrome C]] to [[Oxygen|O]]<sub>[[Oxygen|2]]</sub><br> o 4H<sup>+</sup> from matrix allow the complete [[Reduction|reduction]] of [[Oxygen|O]]<sub>[[Oxygen|2]]</sub> to [[Water|H]]<sub>[[Water|2]]</sub>[[Water|O]]<br> o 4 more H<sup>+</sup> pumped across membrane | • ''Complex IV'' – Cytochrome C Oxidase<br> o 4 electrons transferred from [[Cytochrome C|cytochrome C]] to [[Oxygen|O]]<sub>[[Oxygen|2]]</sub><br> o 4H<sup>+</sup> from matrix allow the complete [[Reduction|reduction]] of [[Oxygen|O]]<sub>[[Oxygen|2]]</sub> to [[Water|H]]<sub>[[Water|2]]</sub>[[Water|O]]<br> o 4 more H<sup>+</sup> pumped across membrane | ||
Revision as of 14:45, 16 October 2012
Electron Transfer Chain The electron transfer chain is a series of protein complexes; NADH-Q oxioreductase, Q-cytochrome C oxioreductase, cytochrome C oxidase and ATP synthase. These components contain certain redox centres, and electrons move to carriers with increasing electron affinity along the chain: 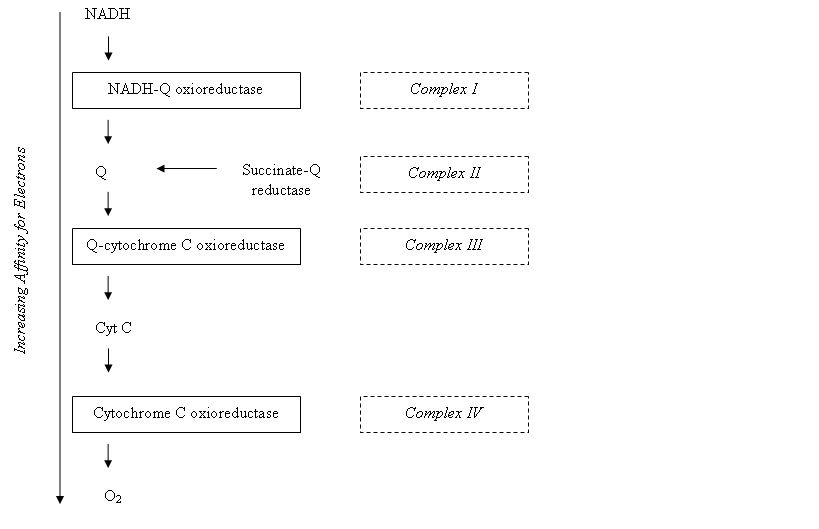
[Q is coenzyme Q, also known as ubiquinone, and carries electrons from NADH and FADH2. It is hydrophobic and diffuses rapidly in the inner mitochondrial membrane.]
• Complex I – NADH-Q oxioreductase
o Transfer of two high-potential electrons from NADH to FMN
o Electrons from FMNH2 transferred to a series of Fe-S clusters
o Electrons from Fe-S clusters shuttled to Coenzyme Q
o Net Effect –
4H+ pumped out of matrix into intermembrane space
2 chemical H+ removed from matrix
• Complex II – Succinate-Q reductase complex
o Succinate dehydrogenase (in Cirtic Acid Cycle) part of succinate-Q reductase complex
o Electrons from FADH2 transferred to Fe-S clusters and then to Q
o Does not pump protons - therefore less ATP is formed by oxidation of FADH2 than NADH
• Complex III – Q-cytochrome C oxioreductase
o Cytochrome C is in all organisms with mitochondrial respiratory chains
o Small soluble protein containing C-type heme
o Carries one electron from Q-cytochrome C oxioreductase to cytochrome C oxidase
o Electrons transferred from QH2 to oxidised cytochrome C (CytCox)
o Mechanism that couples electron transfer is known as the Q Cycle
• Complex IV – Cytochrome C Oxidase
o 4 electrons transferred from cytochrome C to O2
o 4H+ from matrix allow the complete reduction of O2 to H2O
o 4 more H+ pumped across membrane